Linear SHM
Linear SHM: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Spring - Block System, Angular Frequency with Real Spring, Reduced Mass in SHM, Horizontal Oscillations of a Spring Mass System, Vertical Oscillations of a Spring Mass System, and so on.
Important Questions on Linear SHM
If is the displacement of a particle performing SHM, then is equal to its _________ energy.
The K.E of a particle performing simple harmonic motion is _______ whose displacement is .
The kinetic energy and potential energy of a particle exerting simple harmonic motion of amplitude will be equal when displacement is
For a body executing SHM, its potential energy for displacements and are and respectively. Then what is the potential energy at a displacement .
Plot the graph of potential energy versus time for a pendulum performing the simple harmonic motion.
Graph of kinetic energy in terms of displacement in SHM :-
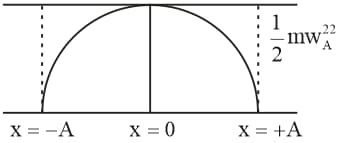
At displacement _____ of a particle executing SHM, has maximum kinetic energy.
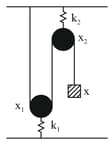
A mass is suspended one by one by two springs of force constants . The time periods of their oscillations are respectively. If the same mass be suspended by connecting the two springs in parallel then the time period of oscillations is .The correct relation is:
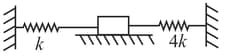
A solid block on a frictionless surface is connected to two rigid supports on the left and right side by springs of spring constants and respectively as shown in the figure. The time spent by the block in a complete cycle of oscillation on the left and the right side of the equilibrium position are and respectively. Which of the following is correct?
A body of mass m is suspended from vertical spring and is set into simple harmonic oscillations of time period . Next the spring is fixed at one end on a smooth horizontal table and same body is attached at the other end. The body is pulled slightly and then released to produce horizontal oscillations of the spring. The time period of horizontal oscillations is
Let be the spring constant of a spring. If the spring is cut into two equal parts, then spring constant of each part is
An uncalibrated spring balance is found to have a period of oscillation of , when a weight is suspended from it, how much does the spring elongate, when a weight is suspended from it? Take
If a watch with a wound spring is taken on to the moon. It
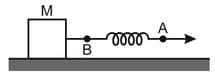
A block of mass is placed on a smooth horizontal surface, and it is pulled by a light spring as shown in the diagram. If the ends and of the spring are moving with and respectively in the same direction and at this moment the rate at which spring energy is increasing is , then what is the value of spring force (in )?
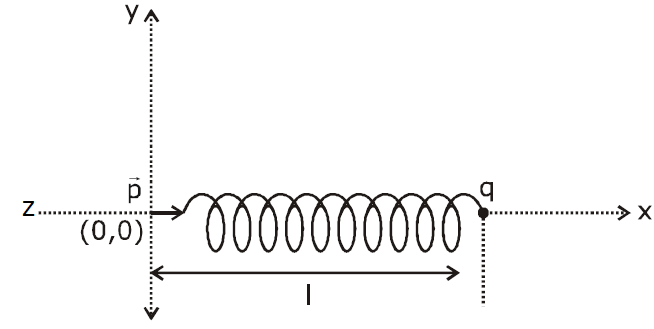
One end of a spring of negligible unstretched length and spring constant is fixed at the origin A point particle of mass m carrying a positive charge is attached at its other end. The entire system is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. When a point dipole pointing towards the charge is fixed at the origin, the spring gets stretched to a length I and attains a new equilibrium position (see figure below). If the point mass is now displaced slightly by from its equilibrium position and released, it is found to oscillate at frequency The value of is
The time period for small vertical oscillations of a block of mass when the masses of the pulleys are negligible and spring constant and is
A mass of is attached to the lower end of a massless spring of force constant , the upper end of which is fixed to a rigid support. Which of the following statement is true?
Two point masses of and are attached to opposite ends of horizontal spring whose spring constant is as shown in the figure. The natural vibration frequency of the system is approximately
An arrangement of spring, strings, pulley and masses is shown in the figure below.
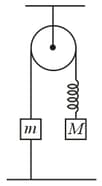
The pulley and the strings are massless and . The spring is light with spring constant . If the string connecting to the ground is detached, then immediately after detachment
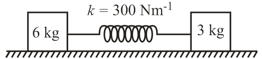
A force constant of ideal spring is . It is loaded with a mass at the lower end the period of its vibration is:
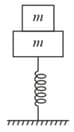
A block of mass is at rest on an another block of same mass as shown in figure. Lower block is attached to the spring, then the maximum amplitude of motion so that both the block will remain in contact is: